How to use a dslr camera for beginners
An In-Depth Beginner's Guide to DSLR Cameras
Introduction: Photography is an art form that allows us to capture and preserve moments in time. For beginners who are eager to explore the world of photography, a DSLR (Digital Single-Lens Reflex) camera offers a versatile tool with exceptional image quality and creative control. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of DSLR cameras, equipping you with the necessary knowledge to start your photographic journey.
How to use dslr camera for beginners
- Understanding DSLR Cameras:
1.1 What is a DSLR Camera?
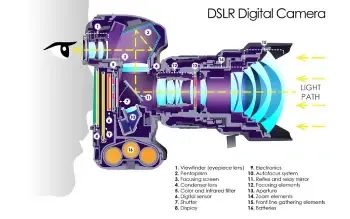
A DSLR camera employs a mirror and prism system that directs light from the lens to an optical viewfinder, enabling photographers to compose images with precision and accuracy.
1.2 Advantages of DSLR Cameras: DSLR cameras offer several advantages over other types of cameras, including interchangeable lenses, superior image quality, extensive manual control, and the ability to capture fast-moving subjects with minimal shutter lag.
- Essential DSLR Terminology:
2.1 Sensor Size: The size of the image sensor within a DSLR camera directly affects image quality and low-light performance. Larger sensors typically produce better image quality and allow for greater control over depth of field.
2.2 Megapixels: The number of megapixels refers to the resolution of the camera's sensor. While higher megapixel counts can offer greater detail, it is important to consider other factors such as sensor size and image processing capabilities for optimal image quality.
- Choosing the Right DSLR Camera:
3.1 Consider Your Needs: Before purchasing a DSLR camera, evaluate your photography goals, preferred subjects, and budget. This will help narrow down your options and ensure that you select a camera that suits your specific requirements.
3.2 Lens Compatibility: One of the advantages of DSLR cameras is the ability to use a variety of lenses. Research the lens options available for the camera you are considering and assess whether they cover the focal lengths required for your desired photography genres.
- Key Features and Controls:
4.1 Shutter Speed: Shutter speed determines the duration for which the camera's sensor is exposed to light. Understanding and controlling shutter speed allows you to freeze fast-moving subjects or create motion blur for artistic effects.
4.2 Aperture: Aperture refers to the size of the camera's lens opening and controls the amount of light that enters the camera. It also affects depth of field, allowing you to emphasize or blur the background of your images.
4.3 ISO Sensitivity: ISO sensitivity determines the camera's ability to capture images in low-light conditions. Higher ISO settings amplify the camera's sensor sensitivity, but may introduce digital noise into the image. Balancing ISO with aperture and shutter speed is essential for achieving optimal exposure.
- Mastering Exposure:
5.1 Metering Modes: DSLR cameras offer various metering modes, such as evaluative, spot, and center-weighted, which measure the available light to determine the camera's exposure settings. Understanding and selecting the appropriate metering mode helps you achieve accurate exposures in different shooting scenarios.
5.2 Exposure Compensation: Exposure compensation allows you to adjust the camera's automatically calculated exposure settings to achieve your desired brightness or darkness level. This feature is particularly useful in challenging lighting conditions or when emphasizing specific elements in your composition.
- Composition and Framing:
6.1 Rule of Thirds: The rule of thirds is a basic principle of composition that involves dividing the image frame into a grid of nine equal sections. Placing key elements along the gridlines or at the intersections creates a visually pleasing and balanced composition.
6.2 Leading Lines: Leading lines are a powerful compositional technique in photography that can guide the viewer's eye and create a sense of depth and movement within an image. These lines can be literal, such as roads, paths, or fences, or they can be implied by elements like architectural features, natural formations, or patterns.
6.2 Leading Lines (Continued): Leading lines are elements within a photograph that guide the viewer's eyes towards the main subject. Utilizing natural or man-made lines, such as roads or railings, adds depth and visual interest to your composition. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to maximize the impact of leading lines on your images.
6.3 Framing: Framing involves using elements within the scene to create a frame around your subject, drawing attention and adding context to the image. This technique can be achieved through architectural structures, natural surroundings, or even through the use of foreground elements. By incorporating framing techniques, you can create a sense of depth and dimension in your photographs.
- Post-Processing and Editing:
7.1 RAW vs. JPEG: DSLR cameras allow you to shoot in RAW format, which captures all the data recorded by the camera's sensor. RAW files offer greater flexibility and control during post-processing compared to JPEG files, which are compressed and processed in-camera. Consider shooting in RAW to unleash the full potential of your images during the editing process.
7.2 Editing Software: To enhance and refine your photographs, familiarize yourself with popular photo editing software such as Adobe Lightroom or Capture One. These tools offer a wide range of editing capabilities, including adjustments to exposure, color balance, sharpness, and the ability to remove unwanted elements.
- Continuous Learning and Practice:
Photography is a skill that develops over time through continuous learning and practice. Experiment with different settings, lighting conditions, and subjects to broaden your understanding of DSLR photography. Additionally, seek inspiration from other photographers, attend workshops, and engage in online communities to gain valuable insights and feedback.
- Maintenance and Care:
9.1 Cleaning: Proper maintenance and care of your DSLR camera are essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regularly clean the camera body and lenses using a soft, lint-free cloth to remove dust, fingerprints, and smudges. Use a blower brush or specialized lens cleaning tools to remove debris from the lens surface.
9.2 Storage: When not in use, store your DSLR camera and lenses in a dry and dust-free environment. Invest in a camera bag or case that provides adequate padding and protection. Avoid exposing your equipment to extreme temperatures or humidity, as these conditions can damage sensitive electronic components.
9.3 Battery Management: Maximize the lifespan of your camera's battery by following proper battery management practices. Fully charge the battery before use and avoid completely draining it before recharging. If the camera is not in use for an extended period, remove the battery and store it in a cool, dry place.
- Expanding Your Gear:
10.1 Additional Lenses: As you gain experience and explore different photography genres, consider expanding your lens collection. Specialized lenses, such as telephoto lenses for wildlife photography or macro lenses for close-up shots, can enhance your creative possibilities and allow you to capture unique perspectives.
10.2 Accessories: Various accessories can complement your DSLR camera and enhance your photography experience. Tripods provide stability for long exposures or when shooting in low-light conditions, while external flashes offer greater control over lighting. Explore options such as filters, remote shutter releases, and camera straps to further customize your setup.
- Understanding Camera Modes:
11.1 Auto Mode: Auto mode allows the camera to make all exposure and focus decisions automatically. While convenient for quick snapshots, it limits creative control. As you gain confidence and knowledge, experiment with other shooting modes to take full advantage of your DSLR's capabilities.
11.2 Manual Mode: Manual mode provides complete control over exposure settings, including shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. This mode allows you to fine-tune every aspect of your image, providing maximum creative freedom. Practice using manual mode to understand the relationship between different settings and their impact on the final result.
- Expanding Your Knowledge:
12.1 Photography Resources: To further enhance your skills and knowledge in DSLR photography, explore various resources such as books, online tutorials, and photography courses. These resources offer valuable insights into composition, lighting techniques, and advanced camera functionalities.
12.2 Critique and Feedback: Seeking feedback and constructive criticism on your work is an invaluable way to grow as a photographer. Share your images with fellow photographers, participate in photography forums, or join local photography clubs to engage in discussions and receive feedback that can help you refine your craft.
- Ethical Considerations:
13.1 Respect for Subjects: When photographing people or private property, it is important to obtain appropriate consent and respect the privacy and dignity of your subjects. Be mindful of cultural sensitivities, and avoid intrusive or disrespectful behavior. Build a rapport with your subjects and aim to portray them in a positive and authentic light.
13.2 Environmental Responsibility: As photographers, we have a responsibility to minimize our impact on the environment. Follow ethical guidelines when photographing wildlife and natural landscapes, ensuring that you do not disturb or harm the subjects or their habitats. Leave no trace by refraining from littering and avoiding damage to delicate ecosystems.
- Legal Considerations:
14.1 Copyright: Respect copyright laws by obtaining permission or licensing when using or sharing the work of others. Similarly, protect your own photographs by understanding your rights as a creator and considering appropriate copyright registrations or watermarks if desired.
14.2 Model Releases: When photographing individuals for commercial purposes, it is important to obtain model releases, which grant you the necessary rights to use their likeness. Familiarize yourself with the legal requirements regarding model releases in your jurisdiction to ensure compliance.
- Embracing Creativity:
15.1 Experimentation: Do not be afraid to step outside your comfort zone and experiment with different techniques, perspectives, and genres. Embrace creativity by trying new approaches, such as long exposures, multiple exposures, or unconventional compositions. Push the boundaries and allow yourself to make mistakes, as they often lead to valuable learning experiences.
15.2 Developing a Signature Style: As you progress in your photographic journey, strive to develop a unique and recognizable style. Experiment with different editing techniques, color palettes, and subject matters to express your artistic vision. Consistency and a distinct style can help your work stand out and make a lasting impression.
- Sharing and Showcasing Your Work:
16.1 Online Platforms: Utilize various online platforms, such as photography websites, social media platforms, and online galleries, to share and showcase your work. Engage with the photography community by participating in discussions, joining photography groups, and collaborating with other photographers.
16.2 Print and Exhibitions: Consider printing your photographs and showcasing them in exhibitions, galleries, or local events. The tangible experience of viewing a printed image can have a profound impact on the viewer and provide a unique opportunity to connect with your audience on a deeper level.
- Enjoying the Journey:
Above all, remember to enjoy the process of photography. It is a form of creative expression that allows you to capture the beauty of the world and share it with others. Embrace the challenges, learn from your experiences, and savor the joy and fulfillment that comes with creating meaningful and captivating images.
- Building a Photography Network:
18.1 Networking with Other Photographers: Connecting with fellow photographers can be immensely beneficial for your growth and development as a photographer. Attend photography events, workshops, and conferences to meet like-minded individuals, exchange ideas, and learn from each other's experiences. Networking can also open up opportunities for collaborations, mentorships, and exposure to different perspectives and styles.
18.2 Engaging with Photography Communities: Join online photography communities and forums to engage in discussions, seek advice, and share your work. These platforms provide a supportive environment where you can receive feedback, gain inspiration, and foster meaningful connections with photographers from around the world.
- Pushing Creative Boundaries: 19.1 Personal Projects: Embark on personal photography projects that challenge you creatively and allow you to explore subjects or themes that resonate with you. These projects provide an opportunity to delve deeper into your photographic vision, experiment with new techniques, and tell compelling visual stories.
19.2 Embracing Diversity: Photography offers a powerful platform to showcase the diversity of the world and celebrate different cultures, perspectives, and experiences. Embrace inclusivity in your work by capturing and highlighting the richness and uniqueness of various communities, landscapes, and individuals.
- Evolving with Technology:
20.1 Staying Updated: Keep abreast of the latest advancements in photography technology, including camera models, lenses, accessories, and post-processing software. Regularly update your knowledge to leverage the capabilities of new tools and techniques that can enhance your photography workflow and creative output.
20.2 Embracing Mobile Photography: With the rise of smartphones equipped with high-quality cameras, mobile photography has gained significant popularity. Embrace the convenience and accessibility of mobile photography by exploring apps, editing tools, and techniques specifically designed for smartphone cameras. This allows you to capture moments on the go and experiment with different photographic styles.
- Overcoming Challenges:
21.1 Embracing Failure: Photography, like any artistic pursuit, comes with its fair share of challenges and failures. Embrace these setbacks as valuable learning experiences and opportunities for growth. Analyze your mistakes, seek constructive feedback, and use them as motivation to improve your skills and develop your artistic voice.
21.2 Pushing through Creative Blocks: Creative blocks are natural occurrences for photographers. When facing a creative slump, try stepping out of your comfort zone, exploring new genres, or taking a break to refresh your perspective. Engage in activities outside of photography that inspire you and ignite your creativity.
- Exploring Different Lighting Techniques:
22.1 Natural Light Photography: Mastering the use of natural light is a crucial skill for photographers. Understand how different lighting conditions, such as golden hour, harsh midday light, or soft diffused light, can impact the mood and atmosphere of your photographs. Learn to observe and manipulate natural light to create stunning and compelling images.
22.2 Artificial Lighting: Expand your skills by delving into artificial lighting techniques. Experiment with on-camera or off-camera flash, continuous lighting, or studio setups to create unique and dramatic lighting effects. Understanding artificial lighting opens up a whole new realm of creative possibilities, especially for portrait, still life, or commercial photography.
- Documenting Travel and Culture:
23.1 Travel Photography: When exploring new destinations, travel photography allows you to capture the essence and spirit of a place. Learn to tell captivating visual stories through your photographs, documenting the landscapes, people, culture, and traditions of the locations you visit. Be respectful of local customs and seek authentic experiences to truly showcase the beauty and diversity of different regions.
23.2 Street Photography: Street photography provides an opportunity to capture candid moments of everyday life in urban environments. It requires observation, quick reflexes, and an eye for interesting compositions. Learn to anticipate and capture decisive moments that convey the energy and character of city streets.
- Niche Photography Genres: 24.1 Wildlife Photography: For nature enthusiasts, wildlife photography offers a chance to capture the beauty and behavior of animals in their natural habitats. Invest in telephoto lenses, study animal behavior, and learn techniques for capturing stunning wildlife portraits and action shots. Respect wildlife and prioritize their well-being by observing ethical guidelines for wildlife photography.
24.2 Astrophotography: Astrophotography allows you to capture the wonders of the night sky, including stars, galaxies, and celestial events. Learn about long exposures, star trails, and image stacking techniques to create stunning images of the cosmos. Experiment with different locations and equipment to capture the awe-inspiring beauty of the universe.
- Finding Inspiration: 25.1 Seeking Inspiration in Art and Culture: Expand your creative vision by drawing inspiration from other forms of art, such as paintings, sculptures, music, or literature. Analyze the use of color, composition, and storytelling in different mediums to inform your own photographic style and narrative.
25.2 Exploring Nature and the Outdoors: Immerse yourself in nature and the great outdoors to find inspiration for your photography. Whether it's a serene landscape, the intricate details of a flower, or the raw power of a waterfall, nature offers endless opportunities for capturing breathtaking images. Practice patience and observation to capture the unique beauty of the natural world.
- Adapting to Changing Environments:
26.1 Event Photography: Develop your skills in event photography by capturing special moments at weddings, concerts, sports events, or corporate functions. Learn to work under challenging lighting conditions, capture candid emotions, and tell a cohesive story through your images.
26.2 Documentary Photography: Documentary photography allows you to tell stories and shed light on social, cultural, or environmental issues. It requires empathy, research, and a commitment to ethical storytelling. By capturing compelling images, you can raise awareness, provoke conversations, and create positive change.
- The Business of Photography:
27.1 Marketing and Branding: If you aspire to pursue photography professionally, understanding marketing and branding principles is essential. Develop a strong online presence through a website or portfolio, create a consistent visual identity, and engage in targeted marketing strategies to attract clients and showcase your work.
27.2 Client Management: Client management is a crucial aspect of running a successful photography business. It involves building and maintaining positive relationships with clients, understanding their needs and expectations, and effectively communicating throughout the entire process.
- Personal Projects and Exhibitions:
28.1 Personal Photography Projects: Engage in personal photography projects that resonate with your interests and passions. These projects allow you to explore themes, experiment with different techniques, and express your unique perspective. Personal projects also serve as a platform for self-expression and can become a portfolio highlight.
28.2 Exhibitions and Gallery Displays: Consider showcasing your work through exhibitions or gallery displays. This provides an opportunity to present your photographs to a wider audience, receive feedback, and gain exposure within the art and photography community. Engage with curators, galleries, and local art organizations to explore exhibition opportunities.
- Embracing Criticism and Feedback:
29.1 Constructive Criticism: Be open to receiving constructive criticism and feedback on your work. Engaging in critiques from experienced photographers or participating in portfolio reviews can provide valuable insights, helping you grow and refine your skills. Develop the ability to objectively evaluate your work and learn from the perspectives of others.
29.2 Responding to Feedback: When receiving feedback, remain open-minded and avoid becoming defensive. Embrace feedback as an opportunity for improvement and self-reflection. Analyze the suggestions and apply them to future projects or image refinement, allowing your photography to evolve and reach new heights.
- Giving Back to the Photography Community:
30.1 Mentorship and Teaching: Share your knowledge and expertise with aspiring photographers by engaging in mentorship programs or teaching photography workshops. Guiding and inspiring others not only contributes to the growth of the photography community but also helps you deepen your own understanding of the craft.
30.2 Photography for Social Change: Utilize your photography skills to support social causes or community initiatives. Offer your services pro bono to nonprofits, charities, or grassroots organizations to document their work, raise awareness, and advocate for positive change. Photography can be a powerful tool to amplify voices and inspire action.
- Collaboration and Teamwork:
31.1 Collaborative Projects: Collaborating with other creative professionals, such as models, stylists, makeup artists, and designers, can elevate your photography to new heights. Engage in collaborative projects to bring different talents together, pool resources, and create impactful visual stories. The synergy of teamwork can lead to innovative and inspiring results.
31.2 Assisting Other Photographers: Offering your assistance to established photographers provides valuable learning opportunities and allows you to gain insights into their workflow and techniques. Assisting not only expands your network but also exposes you to diverse shooting scenarios and professional practices that can enhance your own skills and knowledge.
Expanding into Video: Incorporating video into your skill set can open up additional opportunities in the creative industry. DSLR cameras often have video capabilities that allow you to explore filmmaking, storytelling, and capturing motion. Learn the basics of video recording, editing, and post-production to broaden your skill set and cater to clients' multimedia needs.
Continuous Learning:
33.1 Workshops and Continuing Education: Stay updated with the latest trends, techniques, and industry developments by attending photography workshops, seminars, and continuing education programs. These opportunities offer a chance to learn from experienced professionals, gain new perspectives, and acquire advanced skills that can set you apart in a competitive photography landscape.
33.2 Online Learning Platforms: Leverage online learning platforms and resources to access a vast array of photography courses, tutorials, and informative articles. Platforms such as online academies, photography blogs, and YouTube channels offer a wealth of knowledge at your fingertips, enabling you to learn at your own pace and explore specific areas of interest.
- Mindfulness and Creativity:
34.1 Practicing Mindfulness: Incorporate mindfulness practices into your photography journey to enhance your creativity and connection with the present moment. Being fully present in the act of capturing images allows you to observe details, notice unique perspectives, and express your artistic vision authentically.
34.2 Embracing Serendipity: Be open to serendipitous moments and unexpected opportunities that may present themselves while photographing. Sometimes the most captivating and memorable images arise from unplanned encounters or unforeseen circumstances. Embrace spontaneity and allow your intuition to guide you in capturing these magical moments.
- Balancing Artistic Vision and Client Expectations:
35.1 Effective Communication: When working with clients, develop strong communication skills to understand their vision and expectations. Balancing your artistic vision with client requirements ensures a collaborative and successful outcome that satisfies both parties. Actively listen, clarify expectations, and provide professional guidance to deliver exceptional results.
35.2 Contractual Agreements: Establish clear contractual agreements that outline deliverables, usage rights, and financial terms. Having a well-defined agreement protects your work and ensures a mutually beneficial relationship with your clients. Seek legal advice or utilize industry-standard contracts to protect your rights and establish professional boundaries.
- The Power of Personal Projects:
36.1 Passion Projects: Engage in personal projects driven by your passion and curiosity. These projects allow you to explore new techniques, subject matters, or artistic concepts without the constraints of client expectations. Personal projects keep your creativity alive, ignite your enthusiasm, and serve as a source of inspiration for future endeavors.
36.2 Documenting Personal Journey: Use photography as a tool to document your personal experiences, growth, and emotions. Reflect on your own journey through self-portraits, visual diaries, or storytelling projects. Embrace vulnerability and allow your photography to become a means of self-expression and self-discovery.
As you embark on your photography journey, remember that it is a continuous process of exploration, growth, and self-expression. Embrace new challenges, seek inspiration from various sources, and nurture your
- Preservation and Archiving:
37.1 Digital Asset Management: Implement effective digital asset management practices to organize and preserve your photographic archives. Establish a systematic approach to file naming, folder structure, and metadata tagging to easily locate and retrieve images when needed. Regularly back up your files to multiple storage devices or cloud platforms to safeguard against data loss.
37.2 Print and Physical Preservation: Consider printing and framing your best photographs to create tangible representations of your work. Invest in archival-quality materials and techniques to ensure the longevity and preservation of printed images. Additionally, explore options for showcasing your prints in galleries, exhibitions, or art fairs to reach a wider audience.
- Ethical Considerations:
38.1 Model Releases and Permissions: When photographing people, particularly for commercial purposes, obtain proper model releases and permissions to protect the rights and privacy of individuals featured in your images. Familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations regarding consent and intellectual property rights to ensure ethical and legal practices.
38.2 Cultural Sensitivity: When photographing diverse cultures, communities, or sensitive subjects, approach with respect and cultural sensitivity. Seek permission when necessary and be mindful of the impact your work may have on the subjects and their communities. Responsible and ethical photography fosters understanding and promotes positive representation.
- Experimentation and Risk-Taking:
39.1 Embracing Failure as a Learning Opportunity: Don't be afraid to take risks and experiment with new techniques or unconventional approaches. Embrace failure as a natural part of the creative process and learn from the outcomes. It is through experimentation and pushing boundaries that you can discover unique artistic expressions and develop your own signature style.
39.2 Stepping Out of Your Comfort Zone: Challenge yourself to explore genres, subjects, or styles that are outside of your comfort zone. By venturing into unfamiliar territory, you broaden your horizons, expand your skills, and unlock new creative possibilities. Embrace discomfort as a catalyst for growth and artistic development.
- Self-Care and Well-Being:
40.1 Balancing Work and Rest: Maintain a healthy work-life balance to prevent burnout and nurture your creativity. Allow yourself time for rest, relaxation, and pursuing other interests outside of photography. Taking breaks and caring for your well-being replenishes your energy and prevents creative stagnation.
40.2 Connecting with Nature: Reconnect with nature as a source of inspiration and rejuvenation. Spending time outdoors, exploring natural landscapes, and observing the beauty of the world around you can ignite your creativity and provide a fresh perspective. Nature has a way of grounding us and reminding us of the wonders that can be captured through the lens.
- Cultural Exchange and Travel Photography:
41.1 Immersive Travel Experiences: When traveling to different regions or countries, immerse yourself in the local culture and connect with the people. Engage in meaningful interactions, learn about their traditions, and capture authentic moments that reflect the essence of the destination. Travel photography becomes a powerful medium for cultural exchange and fostering understanding between diverse communities.
41.2 Responsible Tourism: As a travel photographer, prioritize responsible tourism practices to minimize your impact on the environment and local communities. Respect cultural norms, follow guidelines for photographing sensitive locations, and support local businesses and artisans. By promoting sustainable travel, you contribute to preserving the authenticity and integrity of the places you visit.
- Photography as a Tool for Advocacy:
42.1 Social and Environmental Causes: Utilize your photography skills to raise awareness and advocate for social and environmental causes. Document issues such as climate change, human rights, or conservation efforts, highlighting the need for action and inspiring change. Your images can serve as powerful tools to mobilize support and drive positive impact.
42.2 Storytelling for Marginalized Communities: Give a voice to marginalized communities through visual storytelling. Use your photography to shed light on their struggles, resilience, and achievements. Approach these stories with empathy, sensitivity, and a commitment to ethical representation, ensuring that the narratives are dignified and respectful.
- Developing a Signature Style:
43.1 Self-Expression and Artistic Vision: Nurture your artistic vision and strive to develop a signature style that sets your work apart. Experiment with different techniques, compositions, and post-processing styles to discover the visual language that resonates with you. Your unique style becomes a reflection of your personality and perspective as a photographer.
43.2 Consistency and Cohesion: Strive for consistency and cohesion in your body of work. Establishing a visual identity and maintaining a cohesive portfolio helps create a strong brand presence and attracts clients who resonate with your style. Consistency also demonstrates your commitment to your craft and professionalism as a photographer.
Collaboration with NGOs and Nonprofits:
Collaborate with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and nonprofits to use your photography as a tool for storytelling and advocacy. Offer your services to document their projects, initiatives, and impact. These collaborations not only contribute to important causes but also provide opportunities to showcase your work to a wider audience.Leveraging Social Media and Online Platforms:
45.1 Building an Online Presence: Utilize social media platforms and online photography communities to showcase your work and connect with a global audience. Curate a visually appealing online portfolio, engage with followers, and participate in relevant photography hashtags and challenges. Consistent online presence helps expand your reach and attract potential clients or collaborators.
45.2 Engaging with the Photography Community: Interact with fellow photographers, join online photography forums, and participate in critique groups to exchange ideas, receive feedback, and learn from others. Actively engage with the photography community by sharing your knowledge, providing constructive feedback, and supporting emerging talents. Collaboration and mentorship within the community foster growth and mutual inspiration.
- Evolving with Technological Advancements:
46.1 Embracing New Technologies: Stay abreast of technological advancements in photography, such as new camera models, lenses, editing software, and post-processing techniques. Embrace innovation and explore how these advancements can enhance your workflow, expand creative possibilities, and streamline your editing process.
46.2 Experimenting with Emerging Trends: Keep an eye on emerging trends in photography, such as drone photography, virtual reality (VR), or augmented reality (AR) experiences. Experiment with these technologies to push the boundaries of your craft and explore new avenues for creative expression. Being adaptable and open to new tools and techniques ensures that your work remains relevant in a rapidly evolving landscape.
- Professional Development and Networking:
47.1 Attending Photography Conferences and Events: Participate in photography conferences, workshops, and industry events to network with professionals, gain insights from experts, and stay updated on the latest industry trends. These events provide valuable opportunities to connect with potential clients, collaborators, and mentors who can further your career in photography.
47.2 Joining Professional Associations: Consider joining professional photography associations and organizations that provide resources, support, and networking opportunities. These associations often offer educational programs, mentorship initiatives, and platforms for showcasing your work. Active involvement in the photography community demonstrates your commitment to professionalism and continuous learning.
- Diversifying Income Streams:
48.1 Commercial Photography: Explore commercial photography opportunities, such as product photography, corporate events, or editorial assignments. Commercial work can provide a stable income stream and expand your client base beyond individual clients or fine art photography.
48.2 Stock Photography and Licensing: Consider licensing your photographs through stock photography platforms or establishing partnerships with agencies. This allows you to generate passive income by selling usage rights to your images for various purposes, such as marketing campaigns, publications, or websites.
48.3 Teaching and Workshops: Share your expertise and passion for photography by offering workshops, online courses, or one-on-one mentoring. Teaching allows you to monetize your knowledge while empowering others to develop their skills. Additionally, workshops and classes can serve as networking opportunities and contribute to your professional reputation.
- Developing a Business Mindset:
49.1 Business Planning and Marketing: Develop a business plan and marketing strategy to effectively promote your services and reach your target audience. Define your unique selling proposition, identify your ideal clients, and establish pricing and packaging structures that align with your value and market demand.
49.2 Financial Management: Maintain proper financial records, track expenses, and establish clear invoicing and payment processes. Understanding the financial aspects of your photography business ensures profitability and sustainability in the long run. Consider consulting with an accountant or financial advisor to optimize your financial management practices.
- Passion and Perseverance:
Lastly, remember that passion and perseverance are key ingredients for success in the field of photography. Stay true to your love for the art form, remain dedicated to honing your skills, and embrace the inevitable challenges that come with a creative career. The journey may have its ups and downs, but with a resilient mindset and unwavering passion, you can navigate the path to a fulfilling and prosperous photography career.
In conclusion, the world of DSLR photography offers endless opportunities for growth, exploration, and self-expression. By incorporating these additional aspects into your practice, such as cultural exchange, advocacy, collaboration, and business acumen, you can elevate your work, expand your reach, and thrive in the competitive photography industry. Embrace the journey with an open mind, continually seek inspiration, and enjoy the profound impact that photography can have on both yourself and the world around you.